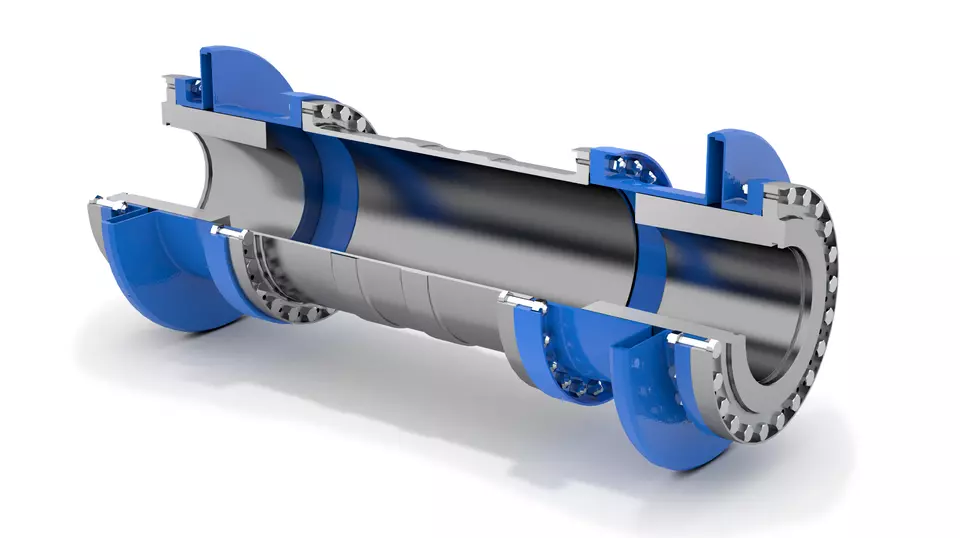
Product Description
Product Description
The main characteristics of a single diaphragm coupling are: high torque bearing, high torque rigidity, and sensitivity; Maintenance free; Zero rotational clearance; A compact coupling with a short total length; Stainless steel coupling diaphragm compensation angle axial deviation; The clockwise and counterclockwise rotation characteristics are the same.
Product Parameters
| Specification | apertured mm | D mm | L mm | A mm | B mm | weight(kg | Allowable speed(rpm) | Nominal torque N.m | Allowable compensation amount | |
| Angular(°) | axial(mm) | |||||||||
| 01 | 8-22 | 68 | 90 | 6.1 | 26 | 0.85 | 20000 | 33 | 1 | ±0.8 |
| 02 | 10-32 | 81 | 95 | 6.6 | 26 | 1.2 | 20000 | 90 | 1 | ±1.0 |
| 03 | 10-35 | 93 | 110 | 8.4 | 29 | 1.7 | 18000 | 173 | 1 | ±1.2 |
| 04 | 10-42 | 104 | 124 | 11.2 | 34 | 2.7 | 15000 | 245 | 1 | ±1.4 |
| 05 | 15-50 | 126 | 152 | 11.7 | 42 | 6.5 | 13000 | 420 | 1 | ±1.6 |
| 06 | 15-60 | 143 | 170 | 11.7 | 48 | 8.9 | 12000 | 772 | 1 | ±1.8 |
| 07 | 20-70 | 168 | 210 | 16.8 | 58 | 15.8 | 10000 | 1270 | 1 | ±2.5 |
Packaging & Shipping
After Sales Service
If during transportation or if the customer receives the goods, opens the packaging and finds any damage, they can resend a new product to the customer.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Can Diaphragm Couplings Operate in High-Temperature or Corrosive Environments?
Yes, diaphragm couplings can be designed and manufactured to operate in high-temperature or corrosive environments, depending on the materials used in their construction. Here’s how diaphragm couplings can handle these challenging conditions:
High-Temperature Environments:
For applications involving high temperatures, manufacturers can use heat-resistant materials for the diaphragm and other coupling components. Some common high-temperature materials include:
- Stainless Steel Alloys: Certain stainless steel alloys, such as Inconel or Hastelloy, are known for their excellent high-temperature properties. These alloys can withstand elevated temperatures without significant deformation or loss of strength.
- Titanium: Titanium is another material that offers good heat resistance. It is lightweight, strong, and can operate at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for certain high-temperature applications.
- Ceramic Coatings: In some cases, manufacturers apply ceramic coatings to the diaphragm or other components to enhance their heat resistance and protect them from thermal degradation.
By using these high-temperature materials, diaphragm couplings can maintain their performance and integrity in environments with extreme heat, such as steel mills, heat treatment furnaces, and power generation plants.
Corrosive Environments:
Diaphragm couplings can also be designed to withstand corrosive environments by using materials that resist chemical attacks. Some options for corrosive environments include:
- Corrosion-Resistant Stainless Steel: Certain stainless steel alloys, like 316L or Duplex stainless steel, offer excellent resistance to corrosion from chemicals and corrosive agents.
- Specialty Coatings: Manufacturers may apply coatings or platings to the coupling components to provide an additional layer of protection against corrosion.
- Non-Metallic Materials: In some cases, non-metallic materials like PTFE (Teflon) or polypropylene may be used for the diaphragm and other components, as they are highly resistant to chemical corrosion.
By using these corrosion-resistant materials, diaphragm couplings can be used in applications such as chemical processing, wastewater treatment, marine environments, and other situations where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
In summary, diaphragm couplings can be engineered to operate in high-temperature or corrosive environments by selecting appropriate materials that offer the necessary heat resistance and corrosion resistance. When specifying a diaphragm coupling for such applications, it is crucial to consider the specific environmental conditions to ensure the coupling’s long-term performance and reliability.

Potential Causes of Failure in Diaphragm Couplings and Prevention Methods
While diaphragm couplings are designed for reliability and durability, certain factors can contribute to their failure over time. Understanding the potential causes of failure and implementing preventive measures can help maximize the lifespan and performance of diaphragm couplings. Here are some common causes of failure and the corresponding prevention methods:
- 1. Misalignment:
- 2. Overloading:
- 3. Corrosion and Contamination:
- 4. Fatigue:
- 5. Improper Installation:
- 6. Excessive Vibrations:
- 7. Lack of Maintenance:
Misalignment between the shafts connected by the diaphragm coupling can lead to increased stresses on the diaphragm and other coupling components. Over time, this can cause fatigue, cracking, or failure of the diaphragm. To prevent misalignment-related failures, ensure that the shafts are properly aligned during installation and perform regular alignment checks during maintenance.
Subjecting the diaphragm coupling to torque levels beyond its rated capacity can lead to premature failure. Overloading can cause excessive deformation of the diaphragm, leading to fatigue and ultimately, failure. To avoid overloading, use diaphragm couplings with appropriate torque ratings for the specific application and ensure that the system operates within the recommended limits.
Exposure to corrosive environments or contaminants can degrade the material of the diaphragm and other coupling components, reducing their strength and integrity. To prevent corrosion-related failures, use diaphragm couplings made from corrosion-resistant materials in environments where exposure to chemicals or moisture is a concern. Regularly inspect and clean the coupling to remove any contaminants that may have accumulated.
Repeated cycles of loading and unloading can cause fatigue in the diaphragm material over time. Fatigue-related failures may manifest as cracks or fractures in the diaphragm. To mitigate fatigue, choose diaphragm couplings made from materials with high fatigue resistance. Regular inspections can also help detect early signs of fatigue-related issues.
Incorrect installation procedures, such as insufficient torque on fasteners or misaligned components, can lead to uneven stresses on the diaphragm coupling, accelerating wear and failure. To prevent improper installation-related failures, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and use appropriate tools and procedures during installation.
Excessive vibrations in the system can lead to premature wear and failure of the diaphragm coupling. To reduce vibrations, ensure that the system is properly balanced and that any issues causing vibrations, such as misalignment or mechanical resonance, are addressed promptly.
Insufficient or irregular maintenance can lead to undetected issues and accelerated wear in the diaphragm coupling. Implement a comprehensive maintenance program that includes regular inspections, lubrication, and alignment checks to identify and address potential problems early.
By addressing these potential causes of failure and taking appropriate preventive measures, such as proper installation, regular maintenance, and using suitable materials, the reliability and lifespan of diaphragm couplings can be significantly improved in various industrial applications.

Are There Any Industry Standards or Certifications for Diaphragm Couplings?
Yes, there are industry standards and certifications that apply to diaphragm couplings, ensuring their quality, performance, and safety. Some of the notable standards and certifications include:
- American Petroleum Institute (API) Standards: API provides standards for various equipment and components used in the oil and gas industry. For diaphragm couplings used in oil and gas applications, compliance with API standards ensures that the couplings meet specific requirements and are suitable for use in demanding environments.
- American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA) Standards: AGMA sets standards for various types of couplings, including diaphragm couplings. These standards cover design considerations, materials, performance, and safety factors, ensuring that couplings adhere to industry best practices.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Standards: ISO has several standards relevant to couplings in general, which can also apply to diaphragm couplings. ISO standards ensure global consistency in terms of design, manufacturing, and performance criteria.
- European Conformity (CE) Marking: Diaphragm couplings intended for sale within the European Economic Area (EEA) must bear the CE marking, indicating that they comply with relevant European Union (EU) directives, including safety and environmental requirements.
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Standards: ANSI sets standards for various industrial equipment, including couplings. ANSI standards provide guidelines for design, materials, and performance, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Compliance: Although not a specific certification for diaphragm couplings, compliance with OSHA regulations is essential to ensure the safety of workers who operate and maintain equipment with diaphragm couplings.
Manufacturers of diaphragm couplings often seek these certifications and comply with relevant industry standards to demonstrate the quality and reliability of their products. Customers and end-users can look for these certifications and standards compliance when selecting diaphragm couplings for their applications, as it provides assurance of the coupling’s performance and adherence to safety requirements.


editor by CX 2024-05-09