Product Description
Product Description
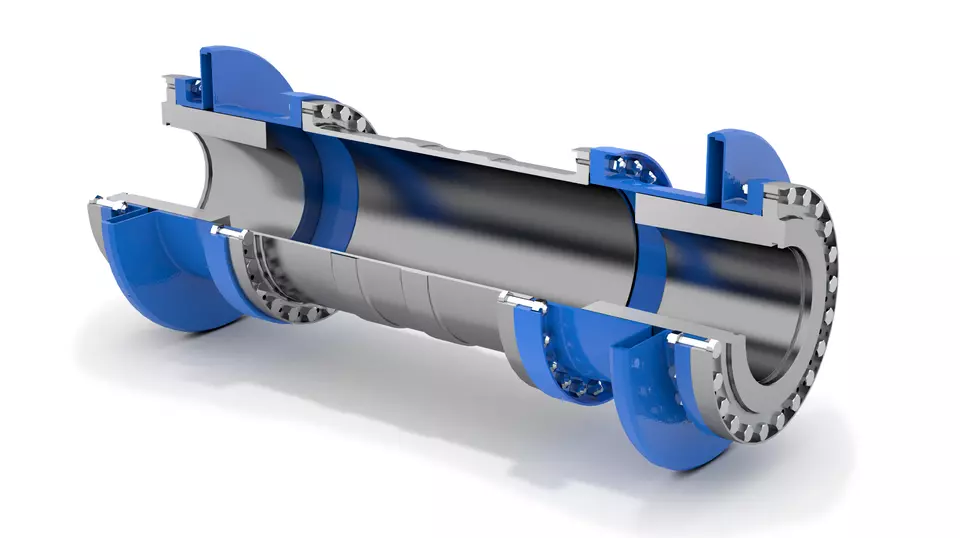
The diaphragm of JM II basic type diaphragm coupling without counterbore is divided into connecting rod type and whole piece type with different shapes. The diaphragm coupling compensates for the relative displacement of the 2 shafts connected by the elastic deformation of the diaphragm. It is a type of metal strong component flexible coupling that does not require lubricating oil, has a compact structure, long service life, no rotational clearance, and is not affected by temperature and oil pollution. It is suitable for shaft transmission in high-temperature, high-speed, and corrosive medium working conditions.
Product Parameters
| Type | Nominal torque Tn |
Peak torque Tmax |
Max Speed nmax |
Bore Diameter d,d1 |
Bore length | D | D1 | t | Torsional rigidity×106 | Mass | Rotary inertia |
||
| J1 type | Y type |
L (recommend) |
|||||||||||
| L | |||||||||||||
| N·m | N·m | r·min-1 | mm | N·m/rad | kg | kg·m2 | |||||||
| JMII1 | 40 | 63 | 10700 | 14 | 27 | 32 | 35 | 80 | 39 | 8±0.2 | 0.37 | 0.9 | 0.0005 |
| 16,18,19 | 30 | 42 | |||||||||||
| 20,22,24 | 38 | 52 | |||||||||||
| 25,28 | 44 | 62 | |||||||||||
| JMII2 | 63 | 100 | 9300 | 20,22,24 | 38 | 52 | 40 | 92 | 53 | 0.45 | 1.4 | 0.0011 | |
| 25,28 | 44 | 62 | |||||||||||
| 30,32,35,38 | 60 | 82 | |||||||||||
| JMII3 | 100 | 200 | 8400 | 25,28 | 44 | 62 | 45 | 102 | 63 | 0.56 | 2.1 | 0.002 | |
| 30,32,35,38 | 60 | 82 | |||||||||||
| 40,42,45 | 84 | 112 | |||||||||||
| JMII4 | 250 | 400 | 6700 | 30,32,35,38 | 60 | 82 | 55 | 128 | 77 | 11±0.3 | 0.81 | 4.2 | 0.006 |
| 40,42,45,48,50,55 | 84 | 112 | |||||||||||
| JMII5 | 500 | 800 | 5900 | 35,38 | 60 | 82 | 65 | 145 | 91 | 1.2 | 6.4 | 0.012 | |
| 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 84 | 112 | |||||||||||
| 60,63,65 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| JMII6 | 800 | 1250 | 5100 | 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 84 | 112 | 75 | 168 | 105 | 14±0.3 | 1.42 | 9.6 | 0.571 |
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| JMII7 | 1000 | 2000 | 4750 | 45,48,50,55,56 | 84 | 112 | 80 | 180 | 112 | 15±0.4 | 1.9 | 12.5 | 0.0365 |
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| 80 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII8 | 1600 | 3150 | 4300 | 50,55,56 | 84 | 112 | 200 | 120 | 2.35 | 15.5 | 0.057 | ||
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| 80,85 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII9 | 2500 | 4000 | 4200 | 55,56 | 84 | 112 | 205 | 120 | 20±0.4 | 2.7 | 16.5 | 0.065 | |
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| 80,85 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII10 | 3150 | 5000 | 4000 | 55,56 | 84 | 112 | 90 | 215 | 128 | 20±0.4 | 3.02 | 19.5 | 0.083 |
| 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | |||||||||||
| 80,85,90 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII11 | 4000 | 6300 | 3650 | 60,63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 100 | 235 | 132 | 23±0.5 | 3.46 | 25 | 0.131 |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| JMII12 | 5000 | 8000 | 3400 | 63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 250 | 145 | 3.67 | 30 | 0.174 | ||
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| JMII13 | 6300 | 10000 | 3200 | 63,65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 110 | 270 | 155 | 5.2 | 36 | 0.239 | |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100,110 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| JMII14 | 8000 | 12500 | 2850 | 65,70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 115 | 300 | 162 | 27±0.6 | 7.8 | 45 | 0.38 |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100,110 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| JMII15 | 10000 | 16000 | 2700 | 70,71,75 | 107 | 142 | 125 | 320 | 176 | 8.43 | 55 | 0.5 | |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| JMII16 | 12500 | 20000 | 2450 | 75 | 107 | 142 | 140 | 350 | 186 | 32±0.7 | 10.23 | 75 | 0.85 |
| 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | |||||||||||
| 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| 130 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| JMII17 | 16000 | 25000 | 2300 | 80,85,90,95 | 132 | 172 | 145 | 370 | 203 | 10.97 | 85 | 1.1 | |
| 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| 130,140 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| JMII18 | 20000 | 31500 | 2150 | 90,95 | 132 | 172 | 165 | 400 | 230 | 13.07 | 115 | 1.65 | |
| 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | |||||||||||
| 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| 160 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| JMII19 | 25000 | 40000 | 1950 | 100,110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | 175 | 440 | 245 | 38±0.9 | 14.26 | 150 | 2.69 |
| 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| 160,170 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| JMII20 | 31500 | 50000 | 1850 | 110,120,125 | 167 | 212 | 185 | 460 | 260 | 22.13 | 170 | 3.28 | |
| 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| JMII21 | 35500 | 56000 | 1800 | 120,125 | 167 | 212 | 200 | 480 | 280 | 38±0.9 | 23.7 | 200 | 4.28 |
| 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | |||||||||||
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| 190,200 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| JMII22 | 40000 | 63000 | 1700 | 130,140,150 | 202 | 252 | 210 | 500 | 295 | 24.6 | 230 | 5.18 | |
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| 190,200 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| JMII23 | 50000 | 80000 | 1600 | 140,150 | 202 | 252 | 220 | 540 | 310 | 44±1 | 29.71 | 275 | 7.7 |
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| JMII24 | 63000 | 10000 | 1450 | 150 | 202 | 252 | 240 | 600 | 335 | 50±1.2 | 32.64 | 380 | 9.3 |
| 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | |||||||||||
| 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| 240 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| JMII25 | 80000 | 125000 | 1400 | 160,170,180 | 242 | 302 | 255 | 620 | 350 | 37.69 | 410 | 15.3 | |
| 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| 240,250 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| JMII26 | 90000 | 140000 | 1300 | 160 | 242 | 302 | 275 | 660 | 385 | 50.43 | 510 | 20.9 | |
| 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | |||||||||||
| 240,250,260 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| JMII27 | 112000 | 180000 | 1200 | 190,200,220 | 282 | 352 | 295 | 720 | 410 | 60±1.4 | 71.51 | 620 | 32.4 |
| 240,250,260 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| 280 | 380 | 470 | |||||||||||
| JMII28 | 140000 | 20000 | 1150 | 220 | 282 | 352 | 300 | 740 | 420 | 93.37 | 680 | 36 | |
| 240,250,260 | 330 | 410 | |||||||||||
| 280,300 | 380 | 470 | |||||||||||
| JMII29 | 160000 | 224000 | 1100 | 240,250,260 | 330 | 410 | 320 | 770 | 450 | 114.53 | 780 | 43.9 | |
| 280,300,320 | 380 | 470 | |||||||||||
| JMII30 | 180000 | 280000 | 1050 | 250,260 | 330 | 410 | 350 | 820 | 490 | 130.76 | 950 | 60.5 | |
| 280,300,320 | 380 | 470 | |||||||||||
| 340 | 450 | 550 | |||||||||||
Packaging & Shipping
After Sales Service
If during transportation or if the customer receives the goods, opens the packaging and finds any damage, they can resend a new product to the customer.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Can Diaphragm Couplings Operate in High-Temperature or Corrosive Environments?
Yes, diaphragm couplings can be designed and manufactured to operate in high-temperature or corrosive environments, depending on the materials used in their construction. Here’s how diaphragm couplings can handle these challenging conditions:
High-Temperature Environments:
For applications involving high temperatures, manufacturers can use heat-resistant materials for the diaphragm and other coupling components. Some common high-temperature materials include:
- Stainless Steel Alloys: Certain stainless steel alloys, such as Inconel or Hastelloy, are known for their excellent high-temperature properties. These alloys can withstand elevated temperatures without significant deformation or loss of strength.
- Titanium: Titanium is another material that offers good heat resistance. It is lightweight, strong, and can operate at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for certain high-temperature applications.
- Ceramic Coatings: In some cases, manufacturers apply ceramic coatings to the diaphragm or other components to enhance their heat resistance and protect them from thermal degradation.
By using these high-temperature materials, diaphragm couplings can maintain their performance and integrity in environments with extreme heat, such as steel mills, heat treatment furnaces, and power generation plants.
Corrosive Environments:
Diaphragm couplings can also be designed to withstand corrosive environments by using materials that resist chemical attacks. Some options for corrosive environments include:
- Corrosion-Resistant Stainless Steel: Certain stainless steel alloys, like 316L or Duplex stainless steel, offer excellent resistance to corrosion from chemicals and corrosive agents.
- Specialty Coatings: Manufacturers may apply coatings or platings to the coupling components to provide an additional layer of protection against corrosion.
- Non-Metallic Materials: In some cases, non-metallic materials like PTFE (Teflon) or polypropylene may be used for the diaphragm and other components, as they are highly resistant to chemical corrosion.
By using these corrosion-resistant materials, diaphragm couplings can be used in applications such as chemical processing, wastewater treatment, marine environments, and other situations where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
In summary, diaphragm couplings can be engineered to operate in high-temperature or corrosive environments by selecting appropriate materials that offer the necessary heat resistance and corrosion resistance. When specifying a diaphragm coupling for such applications, it is crucial to consider the specific environmental conditions to ensure the coupling’s long-term performance and reliability.

How Diaphragm Couplings Handle Torsional Stiffness and Dynamic Balancing in Rotating Machinery
Diaphragm couplings are engineered to address two critical aspects of rotating machinery: torsional stiffness and dynamic balancing. These features ensure efficient power transmission and smooth operation in various industrial applications. Here’s how diaphragm couplings achieve torsional stiffness and dynamic balancing:
- Torsional Stiffness:
- Dynamic Balancing:
Torsional stiffness refers to the ability of a coupling to resist angular deflection or twisting when torque is applied. Diaphragm couplings are designed with a flexible diaphragm made of a high-strength metallic material. This diaphragm connects the two shafts and transmits torque between them.
The design of the diaphragm allows it to flex slightly under load while maintaining its integrity. This controlled flexibility ensures that the diaphragm coupling can handle misalignments and accommodate minor variations in the alignment of the shafts. Despite this flexibility, diaphragm couplings offer high torsional stiffness, ensuring efficient power transmission without significant energy losses due to deformation.
The combination of flexibility and torsional stiffness allows diaphragm couplings to absorb shocks and vibrations, which can occur during start-up or during sudden changes in load. As a result, diaphragm couplings help protect the connected machinery from damage caused by torque fluctuations and torsional vibrations.
Dynamic balancing is crucial to prevent excessive vibrations in rotating machinery, which can lead to premature wear, increased stress on components, and reduced equipment lifespan. Imbalanced rotating parts can cause oscillations and resonance, adversely affecting the overall performance of the system.
Diaphragm couplings are inherently well-balanced due to their symmetrical design and the equal distribution of mass around the center of rotation. This balanced configuration minimizes the generation of vibrations during operation. Additionally, the flexibility of the diaphragm helps dampen any residual vibrations that may arise, further contributing to the dynamic balancing of the system.
In cases where extremely high precision is required, diaphragm couplings can undergo additional balancing processes during manufacturing to fine-tune their dynamic characteristics. This process ensures that the coupling operates optimally even at high rotational speeds.
By efficiently handling torsional stiffness and dynamic balancing, diaphragm couplings contribute to the smooth and reliable operation of rotating machinery across various industries. Their ability to handle misalignments, dampen vibrations, and transmit torque accurately makes them an essential component in many critical applications, such as pumps, compressors, turbines, and more.
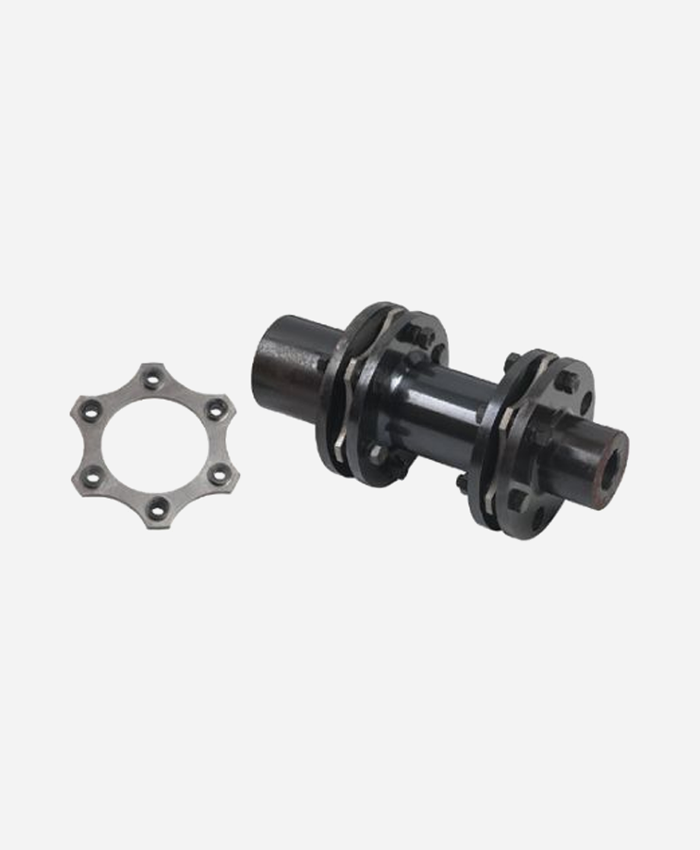

How Do Diaphragm Couplings Handle Misalignment Between Shafts and Reduce Vibrations?
Diaphragm couplings are designed to handle misalignment between shafts and reduce vibrations effectively. Here’s how they achieve these functionalities:
- Misalignment Handling: Diaphragm couplings can accommodate three types of misalignment: angular, parallel, and axial misalignment.
- Angular Misalignment: When the shafts are not perfectly aligned and have angular offset, the flexible diaphragm in the coupling can flex and bend, allowing for relative movement between the shafts without transmitting excessive torque loads or inducing stress on the machinery.
- Parallel Misalignment: In cases where the shafts have parallel misalignment (i.e., horizontal offset), the diaphragm can also flex and move laterally to accommodate the misalignment while maintaining a continuous connection between the two hubs.
- Axial Misalignment: Diaphragm couplings can also handle axial misalignment (i.e., axial displacement), as the flexible diaphragm can compress or elongate slightly to adjust for the axial movement of the shafts.
- Vibration Reduction: Diaphragm couplings are known for their ability to dampen vibrations, which helps in reducing vibration levels in the connected machinery and the overall mechanical system.
- Flexible Diaphragm: The key component that enables vibration reduction is the flexible diaphragm. As the diaphragm flexes in response to misalignment or torque loads, it absorbs and dissipates vibrations, preventing them from being transmitted through the coupling and into the system.
- Natural Frequency: The design of the diaphragm is tuned to have a specific natural frequency, which allows it to effectively dampen and attenuate vibrations within the desired range.
- Material Selection: The choice of material for the diaphragm is crucial in determining its vibration damping capabilities. Certain materials have better vibration-absorbing properties, making them ideal for use in diaphragm couplings.
In summary, diaphragm couplings handle misalignment between shafts by using the flexible diaphragm to accommodate angular, parallel, and axial misalignment. Additionally, they reduce vibrations by utilizing the same flexible diaphragm to dampen and absorb vibrations, enhancing the smooth operation and longevity of the connected machinery and mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2024-04-23